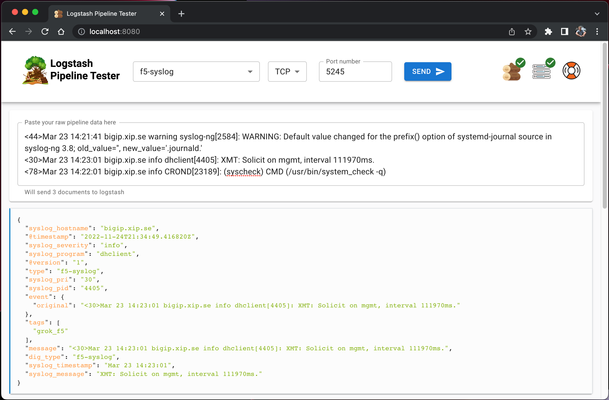
Logstash pipeline tester
Code is community submitted, community supported, and recognized as ‘Use At Your Own Risk’. Short Description A tool that makes developing logstash pipelines much much easier. Problem solved by this Code Snippet Oh. The problem... Have you ever tried to write a logstash pipeline? Did you suffer hair loss and splitting migraines? So did I. Presenting, logstash pipeline tester which givesyou a web interface where you can paste raw logs, send them to the included logstash instance and see the result directly in the interface. The included logstash instance is also configured to automatically reload once it detects a config change. How to use this Code Snippet TLDR; Don't do this, read the manual or checkout the video below Still here? Ok then! 🙂 Install docker Clone the repo Run these commands in the repo root folder:sudo docker-compose build # Skip sudo if running Windows sudo docker compose up # Skip sudo if running WindowsGo to http://localhost:8080on your PC/Mac Pick a pipeline and send data Edit the pipeline Send data Rince, repeat Version info v1.0.0 Docker containers no longer runs as root Vulnerability fix:https://github.com/epacke/logstash-pipeline-tester/releases/tag/v1.0.0 Video on how to get started: https://youtu.be/Q3IQeXWoqLQ Please note that I accidentally started the interface on port 3000 in the video while the shipped version uses port 8080. It took me roughly 5 hours and more retakes than I can count to make this video so that mistake will be preserved for the internet to laugh at. 🙂 The manual: https://loadbalancing.se/2020/03/11/logstash-testing-tool/ Code Snippet Meta Information Version: Check GitHub Coding Language: NodeJS, Typescript + React Full Code Snippet https://github.com/epacke/logstash-pipeline-tester2.1KViews3likes13CommentsPowerShell module for the F5 LTM REST API
Problem this snippet solves: To report an issue with the F5-LTM or F5-BIGIP modules, please use the Issues sections of the GitHub repos (here and here) instead of commenting here. Thanks! This PowerShell module uses the iControlREST API to manipulate and query pools, pool members, virtual servers, and iRules. It aims to support version 11.5.1 and higher, and to conform to the schedule for technical support of versions, though this may eventually prove to become difficult. The module currently includes some functionality that, strictly speaking, is outside the scope of the LTM module. Hence, there is an active effort to wrap this LTM module into a larger BIG-IP module, and relocate that functionality elsewhere within that parent module, as well as expand the scope of functionality to include BIG-IP DNS (formerly GTM) and possibly other areas. Both the LTM module and the parent BIG-IP module are projects on github. Please use these projects to report any issues you discover. Thanks! The module contains the following functions. Add-iRuleToVirtualServer Add-iRuleToVirtualServer Add-PoolMember Add-PoolMonitor Disable-PoolMember Disable-VirtualServer Enable-PoolMember Enable-VirtualServer Get-CurrentConnectionCount (deprecated; use Get-PoolMemberStats | Select-Object -ExpandProperty 'serverside.curConns') Get-F5Session (will be deprecated in future versions. use New-F5Session) Get-F5Status Get-HealthMonitor Get-HealthMonitorType Get-iRule Get-iRuleCollection (deprecated; use Get-iRule) Get-Node Get-BIGIPPartition Get-Pool Get-PoolList (deprecated; use Get-Pool) Get-PoolMember Get-PoolMemberCollection (deprecated; use Get-PoolMember) Get-PoolMemberCollectionStatus Get-PoolMemberDescription (deprecated; use Get-PoolMember) Get-PoolMemberIP (deprecated; use Get-PoolMember) Get-PoolMembers (deprecated; use Get-PoolMember) Get-PoolMemberStats Get-PoolMemberStatus (deprecated; use Get-PoolMember) Get-PoolMonitor Get-PoolsForMember Get-StatusShape Get-VirtualServer Get-VirtualServeriRuleCollection (deprecated; use Get-VirtualServer | Where rules | Select -ExpandProperty rules) Get-VirtualServerList (deprecated; use Get-VirtualServer) Invoke-RestMethodOverride New-F5Session New-HealthMonitor New-Node New-Pool New-VirtualServer Remove-HealthMonitor Remove-iRule Remove-iRuleFromVirtualServer Remove-Pool Remove-PoolMember Remove-PoolMonitor Remove-ProfileRamCache Remove-Node Remove-VirtualServer Set-iRule Set-PoolLoadBalancingMode (deprecated; use Set-Pool) Set-PoolMemberDescription Set-Pool Set-VirtualServer Sync-DeviceToGroup Test-F5Session Test-Functionality Test-HealthMonitor Test-Node Test-Pool Test-VirtualServer How to use this snippet: To use the module, click 'Download Zip', extract the files, and place them in a folder named F5-LTM beneath your PowerShell modules folder. By default, this is %USERPROFILE%\Documents\WindowsPowerShell\Modules. The WindowsPowerShell and Modules folders may need to be created. You will most likely need to unblock the files after extracting them. Use the Unblock-File PS cmdlet to accomplish this. The Validation.cs class file (based on code posted by Brian Scholer) allows for using the REST API with LTM devices with self-signed SSL certificates. Nearly all of the functions require an F5 session object as a parameter, which contains the base URL for the F5 LTM and a credential object for a user with privileges to manipulate the F5 LTM via the REST API. Use the New-F5session function to create this object. This function expects the following parameters: The name or IP address of the F5 LTM device A credential object for a user with rights to use the REST API An optional TokenLifespan value for extending the life of the authentication token past the default 20 minutes You can create a credential object using Get-Credential and entering the username and password at the prompts, or programmatically like this: $secpasswd = ConvertTo-SecureString "PlainTextPassword" -AsPlainText -Force $mycreds = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential "username", $secpasswd Thanks to Kotesh Bandhamravuri and his blog entry for this snippet. There is a function called Test-Functionality that takes an F5Session object, a new pool name, a new virtual server, an IP address for the virtual server, and a computer name as a pool member, and validates nearly all the functions in the module. I've also contributed this code sample for how to gather some basic info about your LTM with this PS module. The module has been tested on: 11.5.1 Build 8.0.175 Hotfix 8 and later 11.6.0 Build 5.0.429 Hotfix 4 and later 12.0 / 12.1 13.0 Code : https://github.com/joel74/POSH-LTM-Rest Tested this on version: 11.519KViews2likes150CommentsBIG-IP Report
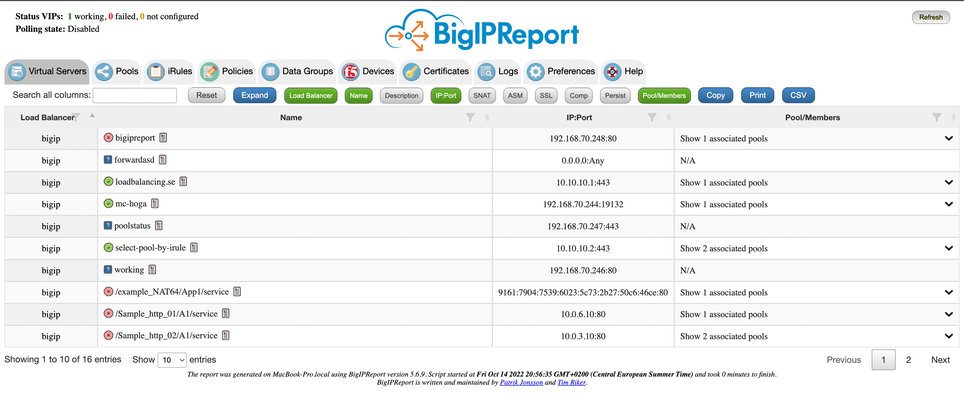
Problem this snippet solves: Overview This is a script which will generate a report of the BIG-IP LTM configuration on all your load balancers making it easy to find information and get a comprehensive overview of virtual servers and pools connected to them. This information is used to relay information to NOC and developers to give them insight in where things are located and to be able to plan patching and deploys. I also use it myself as a quick way get information or gather data used as a foundation for RFC's, ie get a list of all external virtual servers without compression profiles. The script has been running on 13 pairs of load balancers, indexing over 1200 virtual servers for several years now and the report is widely used across the company and by many companies and governments across the world. It's easy to setup and use and only requires auditor (read-only) permissions on your devices. Demo/Preview Interactive demo http://loadbalancing.se/bigipreportdemo/ Screen shots The main report: The device overview: Certificate details: How to use this snippet: Installation instructions BigipReport REST This is the only branch we're updating since middle of 2020 and it supports 12.x and upwards (maybe even 11.6). Downloads (two latest versions): https://loadbalancing.se/downloads/bigipreport-v5.7.11.zip https://loadbalancing.se/downloads/bigipreport-v5.7.10.zip Documentation, installation instructions and troubleshooting:https://loadbalancing.se/bigipreport-rest/ Docker support https://loadbalancing.se/2021/01/05/running-bigipreport-on-docker/ Kubernetes support https://loadbalancing.se/2021/04/16/bigipreport-on-kubernetes/ BIG-IP Report (Legacy) Older version of the report that only runs on Windows and is depending on a Powershell plugin originally written by Joe Pruitt (F5) BIG-IP Report (only download this if you have v10 devices): https://loadbalancing.se/downloads/bigipreport-5.4.0-beta.zip iControl Snapin https://loadbalancing.se/downloads/f5-icontrol.zip Documentation and Installation Instructions https://loadbalancing.se/bigip-report/ Upgrade instructions Protect the report using APM and active directory Written by DevCentral member Shann_P: https://loadbalancing.se/2018/04/08/protecting-bigip-report-behind-an-apm-by-shannon-poole/ Got issues/problems/feedback? Still have issues? Drop a comment below. We usually reply quite fast. Any bugs found, issues detected or ideas contributed makes the report better for everyone, so it's always appreciated. --- Join us on Discord: https://discord.gg/7JJvPMYahA Code : BigIP Report Tested this on version: 12, 13, 14, 15, 1613KViews20likes94CommentsiCR Python Module for iControl REST
Problem this snippet solves: This is a python module to simplify using iControl REST. Install using pip: pip install iCR or retrieve from https://pypi.python.org/pypi?:action=display&name=iCR&version=2.1 As simple as: #!/usr/bin/env python from iCR import iCR bigip = iCR("172.24.9.132","admin","admin") virtuals = bigip.get("ltm/virtual") for vs in virtuals['items']: print vs['name'] This prints out a list of Virtual Servers. Supported methods: init(hostname,username,password,[timeout,port,icontrol_version,folder,token,debug]) get(url,[select,top,skip,filter]) -> returns data or False getlarge(url,size,[select]) -> Used to retrieve large datasets in chunks. Returns data or False create(url,data) -> returns data or False modify(url,data,[patch=True]) -> returns data or False delete(url) -> returns True or False upload(file) -> file is a local file eg /var/tmp/test.txt, returns True or False download(file) -> files are located in /shared/images, returns True or False create_cert(files) -> files is an array containing paths to cert and key. Returns name of cert or False get_asm_id(name) -> name is the name of a policy. Returns an array of IDs or False create_hash(name) -> name is the name of the partition and policy. eg /Common/test_policy. This reduces the need to retrieve an array of hashes from the BIG-IP. Returns a string. get_token() -> this retrieves a BIG-IP token based on the username and password and sets it as the token in use. Returns the token ID or False delete_token() -> This deletes the object token from the BIG-IP and from the object create_transaction() -> creates a transaction and returns the transaction number ID as a string, or False. Subsequent requests will be added to thetransaction until commit_transaction is called. Transaction ID is stored in object.transaction commit_transaction() -> Commits the transaction stored in object.transaction. Returns True or False command(args,[cmd]) -> Runs a command using the arguments string args. Returns the returned output or True on success or False on failure. Note:Be sure to double-escape single quotes eg \\' and single escape double quotes eg \" cmd options are ping/save/load/restart/reboot Module Variables: icr_session - the link to the requests session raw - the raw returned JSON code - the returned HTTP Status Code eg 200 error - in the case of error, the exception error string headers - the response headers icontrol_version - set this to specify a specific version of iControl debug - boolean True or False to set debugging on or off port - set the port ( 443 by default ) folder - set this to create in a specific partition token - use this to set a specific token. If this is set, it will be used instead of basic auth select - use this with get to select the returned data top - use this with get to return a set number of records skip - use this to skip to a specific record number transaction - stores the Transaction ID How to use this snippet: Examples Setup a REST connection to a device #!/usr/bin/env python from iCR import iCR bigip = iCR("172.24.9.132","admin","admin",timeout=10) Create a Virtual Server vs_config = {'name':'test_vs'} createvs = bigip.create("ltm/virtual",vs_config,timeout=5) Retrieve the VS we just created virt = bigip.get("ltm/virtual/test_vs",select="name") print "Virtual Server created: " + virt['name'] Set the timeout bigip.timeout = 20 Now delete the VS we just created delvs = bigip.delete("ltm/virtual/test_vs") Retrieve ASM policy to ID mapping policies = bigip.get("asm/policies",select="name,id") Print a table of ASM policies with learning mode print print "Policy Name Learning Mode" print "------------------------------------------" for item in policies['items']: enabled = bigip.get("asm/policies/" + item['id'] + "/policy-builder",select="learningMode") print '{:32}'.format(item['name']) + enabled['learningMode'] File upload fp = "/home/pwhite/input.csv" if bigip.upload(fp): print "File " + fp + " uploaded" File download file="BIGIP-12.1.2.0.0.249.iso" download = bigip.download(file) if not download: print "File " + file + " download error" SSL Certificate creation In different folder bigip.folder = "TestFolder" files = ("TestCert.crt","TestCert.key") cert = bigip.create_cert(files) if cert: print "Certificate " + cert + " created" Turn on debugging bigip.debug = True Retrieve ASM policy IDs asm = bigip.get_asm_id("dummy_policy") print len(asm) + " IDs returned" print "ID: " + str(asm[0]) Convert an ASM policy name to hash hash = bigip.create_hash("/Common/test-policy") enabled = bigip.get("asm/policies/" + hash + "/policy-builder",select="learningMode") print '{:32}'.format(item['name']) + enabled['learningMode'] Retrieve and use a token bigip.get_token() Delete the token bigip.delete_token() Developed on Python 2.7 but works with v3. Works on TMOS 11.6 onwards though some features may not be implemented, such as tokens. If you use this and have found bugs, would like to discuss it or suggest features then please PM me on DevCentral. Tested this on version: 13.01.1KViews0likes19CommentsGTM return LDNS IP to client
Problem this snippet solves: We do a lot of our load balancing based on topology rules, so it's often very useful to know where the DNS request is actually coming from rather than just the client's IP and the DNS servers they have configured. Especially if they're behind an ADSL router doing NAT or some other similar set up. This rule simply returns the IP address of the LDNS that eventually made the query to the GTM device in the response to a lookup for the WideIP using the rule, as well as logging the response and perceived location. Code : rule "DNS_debug" partition "Common" { when DNS_REQUEST { host [IP::client_addr] log local0.err "Debug address : [IP::client_addr] [whereis [IP::client_addr]]" } }761Views1like1CommentF5 XC reviewing API requests which the GUI sends and a backup of the config with Python/Ansible
Short Description The F5 XC Distributed Cloud GUI in the background sends API requests with JSON body to the system and those requests can be easily reviewed. Problem solved by this Code Snippet If someone wonders how to do some tasks that the XC GUI does the same way but with automation through the API and JSON then this article will help them. Also at the end I have shown how to retrive XC json data with API. How to use this Code Snippet Reviewing the API requests that are generated by the XC GUI. Full Code Snippet There are 3 ways to review the API requests that the GUI generates. On each XC element like for example the load balancer you can click on the JSON and see the JSON code. The JSON code can even be directly edited from the GUI Dashboard! The API documentation can be reviewed directly from the XC GUI. The final option is just to use the browser developer tools and to see what API requests are send by the F5 XC. This feature is now present on most F5 new products like F5OS(Velos/rSeries) and F5 NEXT😉 The XC JSON created objects from the API are a form of a backup configuration. Even if the objects were created from the GUI then API GET requests can be used to retrive their JSON data and this can be saved to a backup file in the form of snapshot. I have used Python with requests library and the url and API key are added as user input arguments. The script can be used to get information like the XC LB or service policies. As example "/api/config/namespaces/default/service_policys". The script will first call an API endpoint to get for example all the load balancer or service policy names and then it will use the names get the config for each individual service policy or load balancer, using a for loop. There is time.sleep(1) to add 1 second slowness between each api request. The code can have the full url like https://{tenant_name}.console.ves.volterra.io/api/config/namespaces/{namespace}service_policysand the api token be added during script execution or the arguments can be input at the start of script execution by commenting outurl = sys.argv[1] and api_token = sys.argv[2] and executing the script like python3 service_policy.py {argument1} {argument2}. The api token by default is hidden using the getpass library for extra security. See Github for the code: Nikoolayy1/xc_api_script: XC API script to retrieve basic json config (github.com) In some cases using Terraform for XC will be best as XC has strong Terraform support as seen at the link below. Ansible can also be used but XC does not have many developed Ansible modules, so in many cases the Ansible URI module will need to be used and the Ansible URI module (ansible.builtin.uri module – Interacts with webservices — Ansible Documentation) in the backgroung is just the python requests or http.client module, as Ansible is python in the background, so better use python directly in that case. XC Terraform: Terraform | F5 Distributed Cloud Tech Docs F5 Distributed Cloud WAAP deployment with Terrafor... - DevCentral Using Terraform and F5® Distributed Cloud Mesh to ... - DevCentral Example Ansible code (even if I said python is better in this case 😀) xc_api_script/xc_ansible at main · Nikoolayy1/xc_api_script (github.com)676Views0likes2CommentsSession Table Export
Problem this snippet solves: This sample goes along with the Tech Tip titled Session Table Exporting With iRules . It creates a mechanism for you to export the data from your session tables for archiving or external reporting. NOTE: This functionality is included in the Session Table Control iRule and is partially rendering here so it has been removed.707Views0likes3CommentsSession Table Control
Problem this snippet solves: This sample goes along with the Tech Tip titled Session Table Control With iRules . It creates an iRules-based HTML application to allow you to view, edit, delete, import, and export your session subtable data. How to use this snippet: Apply to a virtual server with session table entries and you can import/export/edit/delete entries. Code (GitHub gist)1.3KViews0likes5CommentsiCall Script that only runs on Active member
Problem this snippet solves: I had a request to run an iCall script only on the active member in a pair. How to use this snippet: This won't work if you're using active/active via traffic-groups. Code : # Only execute if local BIG-IP is active in failover if {[exec cat /var/prompt/ps1] == "Active"} { tmsh::log "I LIKE SOUP!" } Tested this on version: 12.1709Views0likes2Comments